Human Migration: The Story of a Community
People are constantly moving in and out of countries. People are moving out of countries because of the living consitions, money, and globalization. And sometimes people migrate for the cultural aspect.
http://www.nationalgeographic.com/xpeditions/lessons/09/gk2/humanmigration.html
Sunday, September 27, 2009
Friday, September 25, 2009
Total Fertility Rate
In Canada the fertility rate has increased from 1.59 in 2007 to 1.66 in recent years. It's the highest its been since 1992. 367,864 babies were born in 2007, the highest since 1995. Since 2006, the number increased by 13,247 or 3.7 percent. women the age of 30 - 34 gave birth to 115,415. or a little less than 367,864. Women thirty and over were 50% of all births. Although 1.66 is a good fertility rate it is under what it should be, 2.1.
Net Migration Rate

"Australia’s Population Growing Fast" In Australia the population is growing the fastest its ever been. The population is 21.8 million, and 300,000 are immagrants. The last time the population grew this much was in the 1950's and 60's. But with each million people adds 25 million tons of polution :'( . The growth rate has almost doubled in 5 years.
http://www.redorbit.com/news/science/1757963/australias_population_growing_fast/index.html?source=r_science
Thursday, September 24, 2009

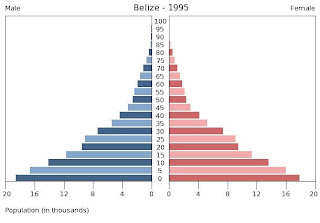
Population Pyramid
The population pyramid shows the population of a country. It will also show us Fertility, Morality, and Migration. The country that I’m demonstrating is Mali. There population is 13,443. There growth rate is 2.6. The fertility rate is 6.6. The crude birth rate is 46. Their births are 642. Their life expectancy at birth is 52. Their infant morality rate is 116. Under five morality rate is 184. The crude death rate is 15. Deaths are 201. The net migration rate is -6. The net number of migrants is -74. http://www.census.gov/ipc/www/idb/informationGateway.php
Tuesday, September 22, 2009
09-22-09

Today we discussed the Demographic Transition. to summarize what it is; Preindustrial- birth and death were very high and population was very low. As we started to urbanize and industrialize, birth and death rate started to slowly go down and population went up slightly. As we were progressing, birth rates were continually getting lower and really close and parallel to the very low death rates. population was very high. When we became Industrialized the population was very high and starting to slope a little bit downward, death rates were extremely low and even (steady), the birth rates are extremely low (BAD) and sloping just below death rates (MORE DEATHS THAN BIRTHS~SCARY!).
I got a considerate button!!!!! YEAH!!!!!!
Monday, September 21, 2009
09-21-09
Friday, September 18, 2009
Thursday, September 17, 2009
Tuesday, September 15, 2009
Population Pyramids
Tuesday, September 15, 2009
11:23 AM
Learning-objectives: teach us components of the pyramid. -gather and analyze info.
• Graphically represent the age and gender distribution of a certain population
• Can be represented by region and by country
• Help human geographers determine what is happening to individual populations across the globe
• Age: younger at the bottom old at the top
• Males on the left and females on the right
• Percentage under the age of 15: global average is 30% , ( Europe ) low is 17%. (Africa) high of 42 percent; high number indicates great potential for future growth, % of population over age 65: identifies need for health care and other social services
• Life expectancy: average number of years a person is expected to live; affected by many factors
• What its good for
• Which country has an overall higher life expectancy
○ Nation B
• Which country has a larger percentage of young population
○ Nation A
• If both countries have the same total population, which will be larger twenty years from now? Why?
○ Nation B because their people life longer and won't die so easily.
Tuesday, September 15, 2009
11:23 AM
Learning-objectives: teach us components of the pyramid. -gather and analyze info.
• Graphically represent the age and gender distribution of a certain population
• Can be represented by region and by country
• Help human geographers determine what is happening to individual populations across the globe
• Age: younger at the bottom old at the top
• Males on the left and females on the right
• Percentage under the age of 15: global average is 30% , ( Europe ) low is 17%. (Africa) high of 42 percent; high number indicates great potential for future growth, % of population over age 65: identifies need for health care and other social services
• Life expectancy: average number of years a person is expected to live; affected by many factors
• What its good for
• Which country has an overall higher life expectancy
○ Nation B
• Which country has a larger percentage of young population
○ Nation A
• If both countries have the same total population, which will be larger twenty years from now? Why?
○ Nation B because their people life longer and won't die so easily.
Monday, September 14, 2009
Wednesday, September 9, 2009
Pros and cons of globalization
The World Bank makes loans to poor countries so they can have a stronger economy.
The International Monetary Fund makes short-term loans to countries that are having financial trouble.
The World Trade Organization works to reduce trade barriers between nations to improve economic globalization and tries to mediate between nations and trading blocks that are arguing over trading.
All three groups are for globalization (pro-globalizers).
The International Monetary Fund makes short-term loans to countries that are having financial trouble.
The World Trade Organization works to reduce trade barriers between nations to improve economic globalization and tries to mediate between nations and trading blocks that are arguing over trading.
All three groups are for globalization (pro-globalizers).
Tuesday, September 8, 2009
1. North America - J
2. Latin America - D
3. The Caribbean - L
4. Sub-Saharan Africa - G
5. Southwest Asia and North Africa (The Middle East)- I
6. Europe - C
7. The Russian Domain - E
8. Central Asia - F
9. East Asia - H
10. South Asia - B
11. Southeast Asia - K
12. Australia and Oceania - A
2. France - Europe 1.United States - North America
3. Iraq - North Africa/Southwest Asia
4. China - East Asia
5. Saudi Arabia - North Africa/Southwest Asia
6. Haiti - The Caribbean
7. India - South Asia
8. Japan - East Asia
9. Venezuela - Latin America
10. Iran - North Africa/Southwest Asia
11. Russia - The Russian Domain
12. The United Kingdom - Europe
13. Israel - North Africa/Southwest Asia
14. Germany - Europe
15. Tibet - East Asia
16. Afghanistan - Central Asia
17. Brazil - Latin America
18. North Korea - East Asia
19. Egypt - North Africa/Southwest Asia
20. Kenya - Sub-Saharan Africa
21. Pakistan - South Asia
22. Vietnam - Southeast Asia
23. Mexico - Latin America
24. Cuba - The Caribbean
2. Latin America - D
3. The Caribbean - L
4. Sub-Saharan Africa - G
5. Southwest Asia and North Africa (The Middle East)- I
6. Europe - C
7. The Russian Domain - E
8. Central Asia - F
9. East Asia - H
10. South Asia - B
11. Southeast Asia - K
12. Australia and Oceania - A
2. France - Europe 1.United States - North America
3. Iraq - North Africa/Southwest Asia
4. China - East Asia
5. Saudi Arabia - North Africa/Southwest Asia
6. Haiti - The Caribbean
7. India - South Asia
8. Japan - East Asia
9. Venezuela - Latin America
10. Iran - North Africa/Southwest Asia
11. Russia - The Russian Domain
12. The United Kingdom - Europe
13. Israel - North Africa/Southwest Asia
14. Germany - Europe
15. Tibet - East Asia
16. Afghanistan - Central Asia
17. Brazil - Latin America
18. North Korea - East Asia
19. Egypt - North Africa/Southwest Asia
20. Kenya - Sub-Saharan Africa
21. Pakistan - South Asia
22. Vietnam - Southeast Asia
23. Mexico - Latin America
24. Cuba - The Caribbean
Thursday, September 3, 2009
Home work
8/31/09 - Globalization-The increasing interconnectedness of people and place throughout the world through converging processes of economic, political, and cultural change.
• HEADINGS- Diversity amid globalization, converging currents of globalization, globalization and geopolitics, environmental concerns, social dimensions.
• Bold print-globalization.
• 9/01/09 - Five Themes of Geography- Environmental Geography, Population and Settlement, Culture Coherence and Diversity, Geopolitical Framework, Economic and Social Development.
• HEADINGS- Diversity amid globalization, converging currents of globalization, globalization and geopolitics, environmental concerns, social dimensions.
• Bold print-globalization.
• 9/01/09 - Five Themes of Geography- Environmental Geography, Population and Settlement, Culture Coherence and Diversity, Geopolitical Framework, Economic and Social Development.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)